
News

News
Recently, one review paper entitled “Application of Solid Catalysts with an Ionic Liquid Layer (SCILL) in PEMFCs: From Half-Cell to Full-Cell” was published at Electrochemical Energy Reviews (IF=31.3). The first author is Xiaojing Cheng, a postdoctoral fellow at Institute of Fuel Cells from School of Mechanical Engineering, and the corresponding authors are Prof. Junliang Zhang and Prof. Shuiyun Shen.

Research topics in application of SCILL in PEMFC
The advantages of zero-emission, high energy efficiency make proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs) a promising option for the future energy conversion devices. In order to address the cost issue caused by Pt-based electrocatalysts, significant efforts have been devoted to the catalyst surface modification by means of solid catalysts with ionic liquid layer (SCILL), which benefits both the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity and the oxygen transport in cathode catalyst layers (CCLs) over the past several years. However, in spite of numerous dramatically enhanced ORR activity tested via rotating disk electrode (RDE) testing, few researches about the application of SCILLs in membrane electrode assembly (MEA) were reported. The underlying reason lies on the well-acknowledged technological gap between the half- and full-cells, which originates from the disparate microenvironments for three phase boundaries. Therefore, the objective of this review is to compare the detailed information of ORR performance boosting in both half- and full-cells, thus deepening the fundamental understanding about the mechanism of SCILL.
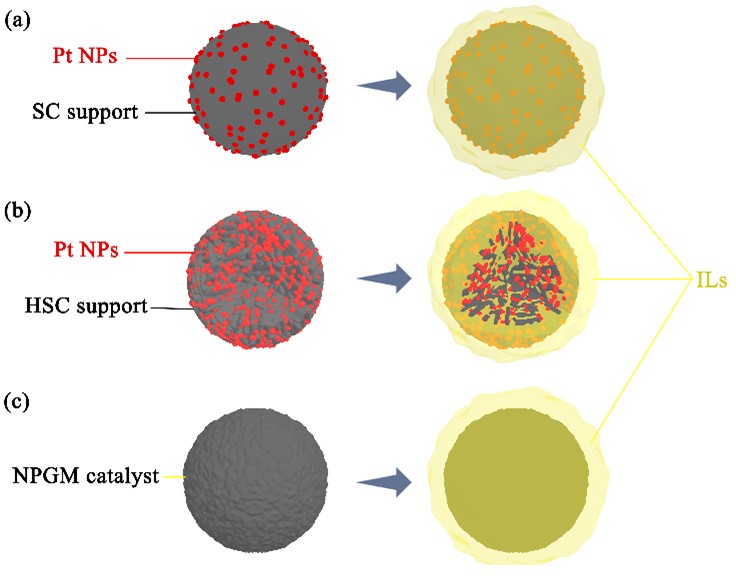
Schematic diagram of (a) SC supported Pt-base catalyst, (b) HSC supported Pt-base catalyst (sectional drawing), (c) NPGM catalyst and the corresponding SCILL catalysts.
In this review, the concept of SCILL and its origin are introduced, then the outstanding electrochemical performance of SCILL catalyst in both RDE and MEA measurements are summarized, and the durability of SCILL catalysts are analyzed concurrently. Subsequently, the suggested mechanism of enhanced ORR activity in half-cells, the improved oxygen transport in full-cells as well as the boosted stability of SCILL catalysts are discussed, while the effect of IL chemical structure, IL loading and operating condition on the performance and lifetime for SCILL catalysts are assessed. Finally, comprehensive conclusions and perspectives are proposed in the last section. It is believed that the new insight presented in this review could provide guidance for the further development of SCILLs in low Pt PEMFCs.
Paper Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s41918-023-00195-5

Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Address: 800 Dongchuan Road, Shanghai
200240